Introduction: an anti-commonsense phenomenon
While ordinary electronic devices often fail to operate at low temperatures due to battery degradation, some DC-DC chargers are able to start up and power up devices at temperatures of -40°C or even lower. This phenomenon, known as ‘Cold Start’, may seem counter-intuitive, but it is a clever result of modern power design. Today, we will reveal the mystery of DC-DC charger cold start!
1. What is dcdc battery charger
Battery charger is an electronic device for charging rechargeable batteries used in electric vehicles, power tools, video games, notebooks, photovoltaic, digital and small portable electronic equipment and electronic appliances, generally by the shell, the power conversion part, the charging detection part, the charging protection part and other components. Its output type is pure DC or pulsating DC. According to the connection method can be divided into wall-plug type and desktop type. According to the type of charging battery can be divided into nickel-cadmium battery charger, nickel-metal hydride battery charger, nickel-zinc battery charger, lead-acid battery charger, lithium battery charger, lithium iron phosphate charger.
2. What is a cold start?
‘Cold start’ refers to the ability of a power supply to activate itself and stabilise its power output under very low input voltage or extreme temperature conditions. For example, when a car is ignited in the middle of winter, the battery voltage may plummet to 6V (nominal 12V), but the DC-DC charger is still able to step up the voltage to supply power to the on-board equipment;
Solar system in the early morning low light, the input voltage is extremely low, but the charger can ‘wake up’ the energy storage battery.
3. DC-DC chargers can be cold start reasons
DC-DC charger cold start is mainly due to its ability to provide stable power output when the battery voltage drops to a very low level. Under cold start conditions, the car battery and engine are in a low temperature state, and starting the engine requires a large amount of current, which will lead to a rapid drop in battery voltage to below 3V or 4.5V in a short period of time. In this case, the traditional 5V or 10V power supply can not provide sufficient voltage support, so it needs to be boosted by the DC-DC charger operation.
4. The specific working principle of DC-DC charger
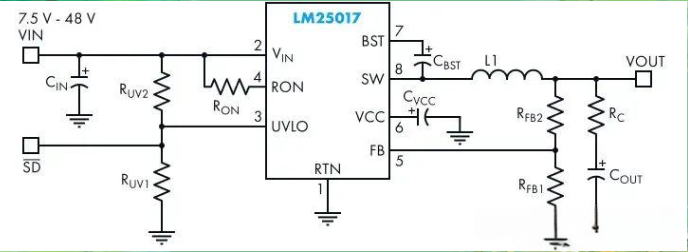
The DC-DC charger achieves cold start by the following steps:
00001. voltage conversion: the DC-DC charger is able to convert the high-voltage DC from the power battery into the required low-voltage DC, usually 12V or 14V, to meet the needs of the vehicle electrical system.
00002. power management: during cold start, the DC-DC charger is capable of detecting changes in the battery voltage and providing a stable output voltage when the voltage drops to ensure that the electrical system works properly.
00003. Energy Recovery: When the vehicle is decelerating or braking, the DC-DC charger is also able to convert the recovered energy into DC power and store it in the battery, further improving the efficiency and reliability of the system.
5. Three Technical Principles of Cold Start
Wide voltage input range design
DC-DC chargers that support cold start usually have an ultra-wide input voltage range (e.g., 4V-40V), so that even if the input voltage briefly drops below the normal value, the internal circuit can still maintain operation.
Technology Implementation:
Buck-Boost topology: automatic switching of buck/boost mode to adapt to input fluctuations;
Low dropout linear regulator (LDO): prioritises power supply to the control chip at very low voltages.
Self-powered ICs and energy harvesting
Critical chips (e.g. PWM controllers) need to ‘survive’ at low voltages:
Bootstrap circuits: Use the initial small current to build up the start-up voltage;
Energy harvesting techniques: ‘squeezing’ small amounts of power from the input side (even from ambient noise).
Low temperature adaptable materials
Wide temperature components: e.g. -40℃~125℃ electrolytic capacitors, cold-resistant MOSFETs;
Low-temperature solder paste soldering: to avoid cracking of solder joints in extremely cold environments.
6. Application Scenarios and Importance of DC-DC Charger
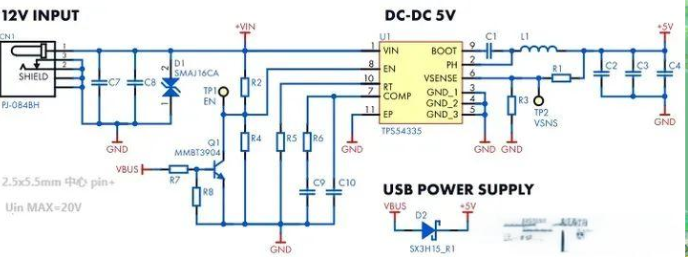
DC-DC charger has a wide range of applications in pure electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles:
- Pure electric vehicles: It is mainly used to convert the high-voltage DC of the power battery into low-voltage DC of 12V or 14V to charge the 12V battery and supply low-voltage electrical equipment of the whole vehicle.
- Hybrid Vehicles: In inefficient operating conditions, such as starting/very low speed, the DC-DC charger can provide the necessary voltage support to ensure the normal operation of the electric motor.
Through these functions, the DC-DC charger not only improves the starting reliability of the vehicle, but also optimises the energy efficiency and ensures stable operation of the vehicle in different operating conditions
Conclusion: Small Charger, Big Wisdom
The cold-start capability of DC-DC chargers reflects the forward-thinking approach to extreme scenarios in power supply design. Whether it's meeting the challenges of the natural environment or fulfilling industrial needs, this technology is quietly pushing the boundaries of energy applications.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media













