High-voltage DC power supplies usually need to be grounded in practical applications to ensure the safety and stability of the power supply. This article will explain in detail from different aspects why high-voltage DC power supplies need to be grounded and how to properly ground them.
1. What is a high-voltage DC power supply
High-voltage DC power supply for communication, also known as HVDC, is a new type of DC uninterruptible power supply system. The high voltage here is relative to the traditional -48V DC communication power supply. DC uninterruptible power supply system.
2. Working principle and functional characteristics
Working principle
The HVDC system is mainly composed of an AC distribution unit, a rectifier module, a battery, a DC distribution unit, a battery management unit, an insulation monitoring unit and a monitoring module. Under normal working conditions, the rectifier module converts the 380V AC output of the AC distribution power supply into a 240V high-voltage DC. The high-voltage DC is supplied to the communication equipment through the DC distribution unit and also charges the battery. When the AC input fails, the DC is supplied to the communication equipment by the battery.
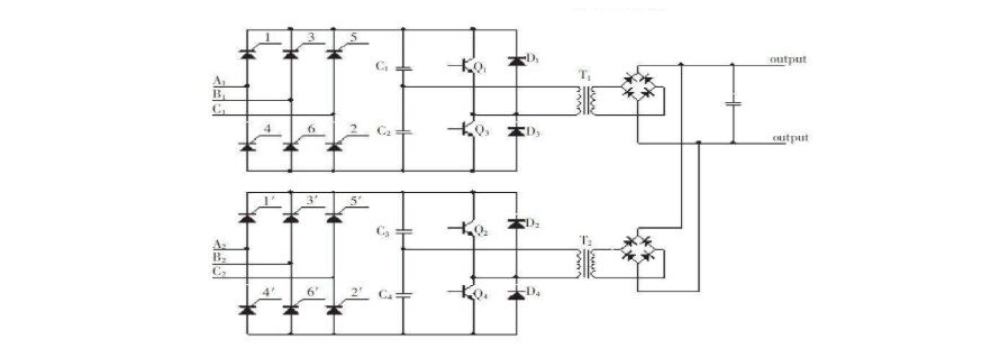
Functional features
2.1 AC power distribution unit
The AC power distribution unit distributes two mains power to each rectifier module through automatic or manual switching; and is equipped with C and D two-pole lightning protection system.
2.2 Rectifier module
The rectifier module is the core part of the system. It converts AC into DC (AC/DC) to supply power to the load and charge the battery at the same time.
2.3 Battery
The battery is the key to ensure uninterrupted power supply. When the AC power is off, the battery supplies power to the load.
2.4 DC power distribution unit
The DC power distribution unit outputs to the column head cabinet through the DC circuit breaker or fuse, and then outputs to each server from the column head cabinet to provide DC power to the server.
2.5 Monitoring module
The monitoring module is the "brain" and "eyes" of the entire system, responsible for monitoring and processing the real-time operation of each unit.
2.6 Battery Management Unit
The battery management unit can detect the terminal voltage of each battery, the internal resistance of the battery pack, the terminal voltage of the battery pack, the charging and discharging current and temperature in real time, and send them to the monitoring module to ensure that the battery pack is in normal working state at any time.
2.7 Insulation Monitoring Unit
The insulation monitoring unit can monitor the insulation status of the DC bus and the output branch to the ground in real time to ensure the personal safety of the operator.
3. Why does the high-voltage DC power supply need to be grounded?
3.1. Protect the safety of equipment and personnel: The grounding of the high-voltage DC power supply can effectively reduce the risk of equipment failure and electric shock. When the equipment fails such as leakage, the fault current is introduced into the ground through grounding to prevent the current from passing through the human body or other equipment, thereby protecting the safety of equipment and personnel.
3.2. Reduce electromagnetic interference: The high-voltage DC power supply may generate strong electromagnetic interference. Grounding can reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference on surrounding equipment and systems. Through grounding, electromagnetic waves can be scattered and absorbed by the ground, reducing electromagnetic radiation.
3.3. Prevent static electricity accumulation: In high-voltage DC power supply systems, static electricity is easily generated due to the accumulation of charges and partial discharge. Grounding can timely conduct these static electricity to the ground to avoid static electricity accumulation causing spark discharge and equipment failure.
3.4. Stabilize voltage and current: During the operation of high-voltage DC power supply, the voltage and current will be unstable due to load changes and fluctuations of the power supply itself. Through grounding, the impact of power supply fluctuations on the system can be reduced, providing more stable voltage and current output.
3.5. Compatible with other systems: Many high-voltage DC power supply systems need to be connected to other low-voltage DC or AC systems. Grounding can reduce the potential difference between these systems and provide better electrical compatibility.
4. How to ground a high-voltage DC power supply?
4.1. Ground connection: High-voltage DC power supplies usually need to use a ground connection to connect the "ground" end of the power supply to the underground conductor to form a low-impedance current loop. The ground wire should select a conductor material that meets the requirements, with good conductivity and corrosion resistance to ensure effective guidance of fault current.
4.2. Ground wire conductivity test: The conductivity of the grounding facility is the key, and regular tests should be performed to ensure good connection and conductivity of the ground wire. The test method can be carried out using a ground resistance tester or other test equipment to ensure that the ground wire impedance meets the relevant specifications.
4.3. Shell grounding: The shell of the high-voltage DC power supply usually also needs to be grounded to reduce the impact of the shell on the electromagnetic radiation and leakage current of the surrounding environment. The shell grounding can be connected to the ground wire or use an independent grounding electrode.
4.4. Grounding electrode selection: The grounding electrode is a key component for conducting current into the ground, and the appropriate electrode type and layout should be selected. Common grounding electrodes include metal rods, buried electrode meshes, and extremely deep holes. Select the appropriate grounding electrode type according to the specific situation.
4.5. Grounding resistance control: The grounding resistance of the high-voltage DC power supply should meet the requirements of relevant standards and specifications. Too large grounding resistance will lead to poor grounding effect, and too small grounding resistance may cause additional fault current. The size of the grounding resistance can be controlled by reasonably configuring the grounding electrode and controlling the soil conductivity.
4.6. Maintenance and inspection: The grounding system of the high-voltage DC power supply should be regularly maintained and inspected to ensure that the grounding resistance is normal and there is no corrosion or loosening of the ground wire and grounding electrode. Regular inspection and maintenance can improve the reliability and stability of the grounding system and ensure the safe operation of the power supply.
In summary, in order to ensure safety and stability, high-voltage DC power supplies usually need to be grounded. Grounding can protect the safety of equipment and personnel, reduce electromagnetic interference, prevent static electricity accumulation, stabilize voltage and current, and be compatible with other systems. Correct grounding methods include ground connection, ground continuity test, shell grounding, ground electrode selection, ground resistance control, and maintenance and inspection of the grounding system. Only through reasonable grounding design and operation can the safe operation of high-voltage DC power supplies be ensured.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media













