Niche Technologies Empower: Short Circuit Prevention Assembly Solutions for Miniaturized AC/DC Power Supplies
In the era of rapid electronic device upgrading toward lightweight and high-density designs, miniaturized AC/DC power supplies serve as the core power supply units, whose reliability directly dictates the operational stability of terminal products. Short circuits, as the most fatal failure mode for such power supplies, not only lead to the burnout of power modules but also may cause the paralysis of the entire electronic system. Unlike the conventional insulation measures widely discussed in the industry, several niche yet highly effective assembly processes have demonstrated unique advantages in mitigating short circuit risks. They not only adapt to the structural constraints of miniaturized products but also eliminate short circuit hazards at the source.
Pin Micro-Pitch Precision Positioning: Lay the Foundation for Short Circuit Prevention
The extremely compact component layout in miniaturized AC/DC power supplies often results in pin spacing reduced to less than 1.0mm. Traditional manual insertion is prone to pin misalignment, crossing, and other issues, which hidden dangers of short circuits. The adoption of laser-assisted positioning combined with vacuum adsorption transfer technology can control pin positioning accuracy within ±0.05mm. This process establishes a 3D coordinate model of components through laser scanning, achieving precise alignment with the preset pad positions on the PCB. Subsequently, vacuum nozzles gently grasp the components for transfer, avoiding mechanical damage and positional deviations caused by manual operations.
To further enhance insulation protection, flexible conductive rubber pads are used to wrap the root of the pins. These pads not only absorb thermal stress during welding but also form an insulating barrier under micro-pitch conditions, effectively reducing the possibility of discharge short circuits between pins. Compared with the commonly used rigid insulation sleeves, flexible conductive rubber pads offer better adaptability to the compact space of miniaturized power supplies, ensuring that there is no interference with the assembly of adjacent components while providing reliable insulation. This process, though not yet widely adopted in mass production, has proven its value in high-precision power supply manufacturing, significantly reducing short circuit risks caused by pin-related issues.
Selective Conformal Coating: Precision Insulation Without Compromising Performance
The traditional conformal coating process involves full-board coating of the power PCB to achieve insulation, but in miniaturized structures, excessively thick coatings can lead to "bridging" between component pins, thereby increasing the risk of short circuits. The selective conformal coating process breaks this conventional approach by utilizing high-precision spray valves to target high-risk areas in the power module for coating, such as high-voltage capacitor pins, rectifier bridge solder joints, and MOSFET drain electrodes. Modified silicone resin materials with low viscosity and high dielectric strength are selected for the coating, with the thickness strictly controlled between 20-50μm. This precise coating thickness not only effectively blocks leakage short circuits caused by dust and moisture intrusion but also avoids affecting the heat dissipation and pin conductivity of components due to coating accumulation. In addition, the localized coating design reduces material usage and lowers production costs compared to full-board coating. For miniaturized AC/DC power supplies operating in harsh environments such as high humidity or dusty conditions, this process provides targeted insulation protection, ensuring long-term stable operation without increasing the overall size of the power supply.
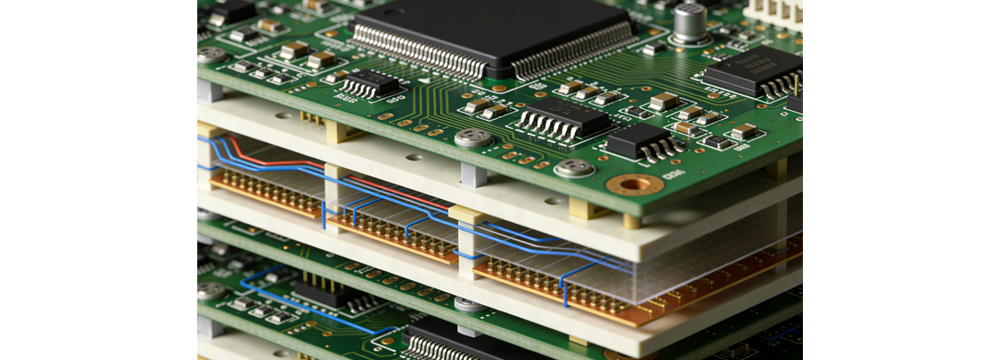
3D Layered Wiring & Insulation Spacing: Optimize Spatial Insulation Efficiency
The internal structure of miniaturized power supplies often adopts a multi-layer PCB stacking design to save space. However, traditional planar wiring is prone to cross-overlapping of lines between different layers, increasing the risk of breakdown short circuits. The 3D layered wiring process optimizes the line routing through 3D wiring simulation software, separating high-voltage circuits from low-voltage circuits and AC loops from DC loops on different layers. Ultra-thin ceramic insulation sheets, with a thickness of only 0.1-0.3mm, are embedded between layers to provide reliable insulation.
Ceramic insulation sheets offer excellent high-temperature resistance and high dielectric strength, making them suitable for the high-temperature operating environment inside power supplies without occupying excessive space. Furthermore, customized insulation brackets are installed between components and the PCB to maintain a safe distance of 3-5mm between heat-generating components and the circuit board. This not only reduces the aging effect of heat conduction on insulation materials but also prevents short circuits caused by direct contact between component pins and PCB copper foil. The combination of 3D layered wiring and insulation spacing effectively resolves the conflict between space utilization and insulation safety in miniaturized AC/DC power supplies.
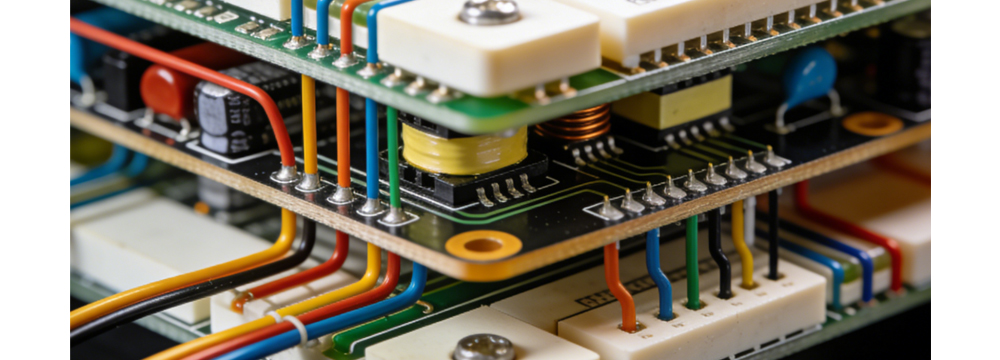
Ultrasonic Precision Welding: Reliable Connection to Avoid Solder-Related Short Circuits
In miniaturized AC/DC power supplies, traditional soldering is prone to cold solder joints and solder bridging. Particularly at micro-solder joints, excessive solder overflow can easily cause short circuits between adjacent pins. The ultrasonic precision welding process replaces traditional soldering, reducing the probability of short circuits from the connection method. This process utilizes high-frequency vibration of 20-40kHz to generate frictional heat on the welding surface, achieving metallurgical bonding between metal atoms under pressure. The resulting welds have no solder overflow, offering high joint strength and stability. Suitable for key connection parts such as internal leads and terminals of power supplies, as well as transformer windings and pins, the welding temperature is below 200℃, avoiding damage to surrounding components and insulation materials caused by high temperatures. Additionally, no flux is required during the welding process, reducing the hidden danger of leakage short circuits caused by residues. This environmentally friendly and reliable welding method is especially suitable for high-density and miniaturized structural design requirements, effectively improving the anti-short circuit performance of power supplies while ensuring assembly efficiency. These niche assembly processes, though not yet mainstream in the industry, have demonstrated significant advantages in short circuit protection for miniaturized AC/DC power supplies. By addressing key aspects such as positioning accuracy, insulation protection, spatial layout, and connection methods, they specifically tackle the short circuit risks associated with miniaturized designs, providing robust technical support for the high reliability of power modules. As electronic devices continue to demand higher levels of miniaturization and stability from power supplies, these niche technologies are expected to gain wider adoption. They will drive the AC/DC power supply industry toward safer, more efficient, and more reliable development, offering innovative solutions for the continuous advancement of electronic products in various fields.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media













