In the field of power supply design, the topology selection of DC-DC converter directly determines the safety, efficiency, and cost of the entire system. As two core architectures, isolated and non-isolated converters may seem to differ only in "the presence or absence of electrical isolation". In reality, however, they vary significantly in application scenarios, performance characteristics, and design complexity. Choosing the wrong type will not only increase development costs but also create potential safety hazards. This article will help engineers fully understand the differences between the two from three dimensions: core distinctions, applicable scenarios, and selection principles.
I. Core Differences: Isolation Barrier Is the Key Factor
The essential difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converters lies in whether there is electrical isolation between the input and output sides. This difference is determined by the topological structure, which in turn affects the product performance and scope of application.
1. Isolated DC-DC Converters
Topological Basis: Adopt topologies such as flyback, forward, push-pull, and full-bridge. Electrical isolation between input and output is achieved through high-frequency transformers, and the turns ratio of the transformer can also flexibly adjust the output voltage.
Core Advantages:
Electrical safety is of paramount importance. Isolation barriers are crucial for ensuring safety. They prevent accidental contact between the input and output sides. This means that even if a fault occurs on the high-voltage side, it will not cause harm to personnel or damage equipment on the low-voltage side. Electrical safety is especially important in places providing medical services, such as hospitals, and in factories with high-voltage systems. These locations must ensure a high level of safety.
This thing is really good, at dealing with interference. It can handle spikes and other bad signals that come from the power grid. This makes the whole system a lot more stable even when there are a lot of things going on around it. The Anti-Interference Capability of this thing is very strong.
The Flexible Adaptation to Multiple Voltages is really useful. It does this by changing the transformer turns ratio. This means you can have one input and many outputs. So the Flexible Adaptation to Multiple Voltages can meet the voltage needs of loads. The Flexible Adaptation to Multiple Voltages is very helpful, in this way.
Limitations:
The thing that makes the cost higher is that we need to add some parts like transformers and optocouplers. These extra parts make the hardware more expensive. They also make it harder to lay out the printed circuit board. This is because the transformers and optocouplers are isolation components that are added to the system. The addition of these isolation components, like transformers and optocouplers is what increases the cost.
The transformer is not as efficient as kinds of converters. This is because the core and the windings of the transformer lose some energy. As a result the transformer can only convert energy with an efficiency that's 2 to 5 percent lower than non-isolated converters. This means that non-isolated converters are a little better at converting energy than transformersre. The efficiency of transformers is a bit of a problem because of the core loss and the winding loss. Transformers have these losses. That is why they are not as efficient, as non-isolated converters.
2. Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters
Topological Basis: This is about topologies, like Buck that steps down Boost that steps up and Buck-Boost that does both step up and step down. The input side and the output side of these things are connected directly through power devices. There is no barrier to keep them electrically separate.
Core Advantages:
The thing about this is that it is really cost effective. It does not have things, like transformers and isolated drivers. This means it costs less to make the hardware. The circuit is also simple and easy to put into things. This makes the cost even lower. The High Cost-Effectiveness of this is very good because of these things.
The thing about conversion efficiency is that it really helps to cut down on the loss of isolation components. This means that the efficiency is usually than 90 percent. Some models that use a lot of power can even do better than that. Get over 95 percent. High conversion efficiency is clearly very useful, for high-power models.
The Compact Size of this thing is really useful. It does not have the problem of being too big like transformers do. This means it can be made into a package. This is great for things like devices that do not have a lot of space. Portable devices have strict rules, about how much space they can take up.
Limitations:
Safety Risks: The Safety Risks of equipment are a concern. The input and the output of the equipment have something in common. If there is a problem with voltage on the input side of the equipment it can easily affect the output side of the equipment. This can be very bad for the equipment and the people using the equipment. The Safety Risks are that people can get hurt and the equipment can get damaged if there is a high-voltage leakage, on the input side of the equipment.
Weak Anti-Interference Capability: It cannot block common-mode interference. In strong electromagnetic interference environments, the output ripple is prone to exceeding standards, affecting the operation of sensitive components at the back end.
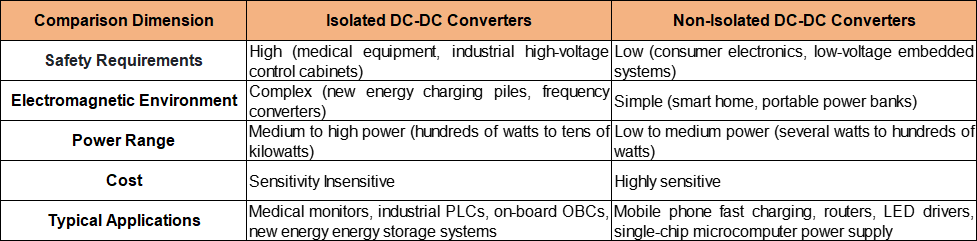
II. Comparison of Applicable Scenarios: Selecting the Right Type Is the Core
The differences between the two types of converters determine their application boundaries. Blind selection will lead to reduced system stability or unnecessary cost waste.
III. Selection Principles: Three Steps to Optimal Solutions
In actual projects, engineers can follow the three-step principle below to quickly determine the selection direction between isolated and non-isolated converters.
1. Prioritize Evaluating Safety and Compliance Requirements
This is the primary premise for selection. If the application scenario involves human contact (e.g., medical equipment), high-voltage power grid connection (e.g., industrial frequency converters), or needs to meet safety standards such as IEC 61558 and UL 60950, isolated DC-DC converters must be selected. On the contrary, for low-voltage non-contact scenarios (e.g., smart home devices), non-isolated converters are a more economical choice.
2. Analyze Electromagnetic Interference and System Stability Requirements
If the system operates in a strong electromagnetic interference environment (e.g., factory workshops, new energy vehicles), the anti-interference capability of isolated converters can better ensure stable system operation; for low-interference laboratory or consumer electronics scenarios, the high cost-effectiveness of non-isolated converters is more prominent.
3. Balance Cost, Efficiency and Size Constraints
On the premise of meeting safety and stability requirements, further weigh the project needs:
Sensitive to cost and size → Non-isolated type;
High requirements for power and reliability → Isolated type.
IV. Conclusion
The core difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converters lies in the presence or absence of an electrical isolation barrier. This difference leads to a series of performance distinctions such as safety, anti-interference, cost, and efficiency, which ultimately determine their application boundaries.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media