An alternator rectifier is a key component in a power system whose main task is to convert alternating current (AC) power to direct current (DC) power. This process is critical for a variety of application scenarios, especially in high-precision equipment and systems that require a stable DC power supply.

Functions and Importance of Rectifiers.
The output of an alternator is alternating current, and this current is widely used in many power transmission and distribution systems. However, many modern electronic devices and precision instruments require DC power for performance and efficiency. DC power has less energy loss during transmission and is voltage stabilized, making it more suitable for precise control. It is against this background of demand that rectifiers come into play, converting AC power into DC power to meet the power needs of different devices.
The basic principle of rectifier operation.
Rectifiers use semiconductor devices (e.g., diodes, thyristors) to fulfill their core function of unidirectional conductivity, which allows current to flow in only one direction. These semiconductor devices are arranged in a specific circuit configuration as follows:
Half-wave rectifier: contains only one diode and can rectify only half the cycle of the alternating current. Although simple and low cost, it is not very efficient and the output current contains more ripple.
Full-wave rectifier: A bridge structure (bridge rectifier) consisting of four diodes is used, which is able to rectify the full cycle of the input alternating current, and the output DC is smoother and more efficient.
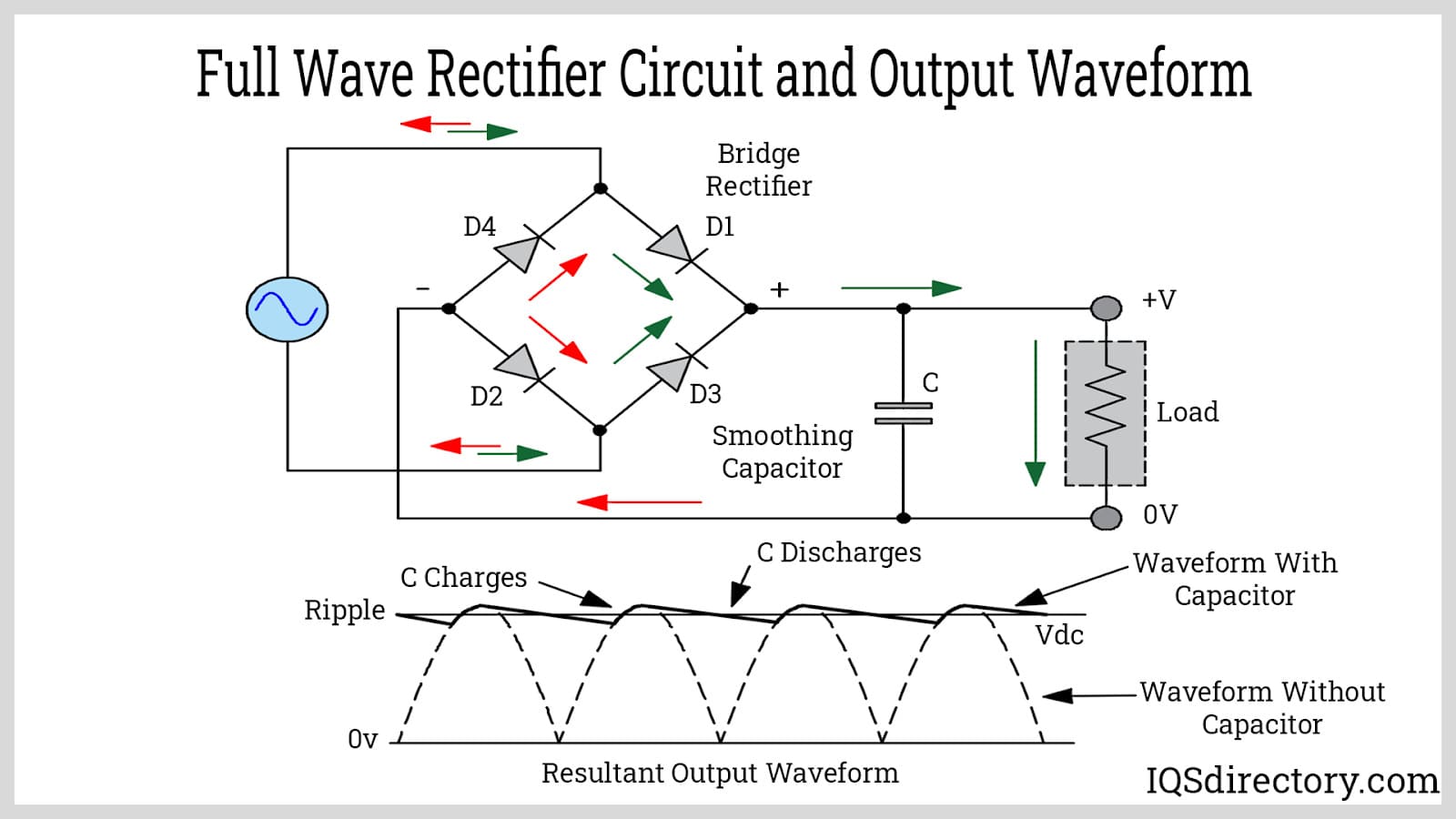
Technologies to ensure smooth power output.
The rectifier ensures smooth power output through the following technologies:
Highly efficient filtering technology: The DC power generated during the rectification process usually contains ripples that can interfere with the normal operation of equipment. The use of capacitors and inductors to form a filter circuit can effectively smooth the output DC power and improve the quality of power.
Advanced Feedback Regulation System: Modern rectifiers are often equipped with a feedback system that automatically adjusts the output voltage according to real-time changes in the load, ensuring the continuity and security of the power supply.
Thermal management design: Due to the energy conversion during the rectification process, the rectifier itself may generate heat. A good thermal management system (e.g., heat sink, fan cooling) is the key to ensure that the rectifier works stably for a long time.
Practical Application Case Analysis.
Take medical devices as an example, these devices usually have very high requirements on the quality of power supply. For example, in equipment such as X-ray machines and cardiac monitors, any small fluctuation in power can affect the accuracy of diagnostic results. The use of high-quality rectifiers with precise filtering and voltage stabilization techniques can effectively reduce power fluctuations and ensure the accuracy of medical diagnosis and patient safety.
Conclusion
Alternator rectifiers ensure a high degree of stability in power output through their highly efficient conversion mechanism, advanced filtering and voltage stabilization techniques. Whether in industrial applications, medical equipment or electronic products in daily life, rectifiers are indispensable key components to guarantee the quality of power supply. As technology continues to advance, the performance and efficiency of rectifiers will continue to improve to meet more demanding power needs.






