 In the tests of power grids, UPS, switching power supplies, rectifiers, frequency converters, inverters, motors, etc., in addition to paying attention to some basic parameters such as voltage, current and power, the other thing that people pay the most attention to should be the culprit of many accidents - harmonics. So what are harmonics? What are the classifications of harmonics? What are its hazards?
In the tests of power grids, UPS, switching power supplies, rectifiers, frequency converters, inverters, motors, etc., in addition to paying attention to some basic parameters such as voltage, current and power, the other thing that people pay the most attention to should be the culprit of many accidents - harmonics. So what are harmonics? What are the classifications of harmonics? What are its hazards?

●What is fundamental wave
Before introducing "harmonics", we must first understand a term - fundamental wave. The definition of "fundamental wave" in the online search is as follows:
The lowest frequency component of a composite wave. In a complex periodic oscillation, it contains fundamental waves and harmonics. The sine wave component equal to the longest period of the oscillation is called the fundamental wave. The frequency corresponding to this period is called the fundamental frequency.
As shown in Figure 1, it is a fundamental wave signal. If a signal only has the "fundamental wave", then it is a perfect signal, but in reality this is impossible. The most mixed among them is harmonics. As the saying goes, a dragon gives birth to nine sons, each with its own characteristics. It can be said that the fundamental wave is orthodox, and the harmonic is like the "睚眦" among the "nine sons", with the characteristics of "bloodthirsty and fond of fighting, engraved on the knife ring, sword handle and swallowing mouth", so what is harmonic?
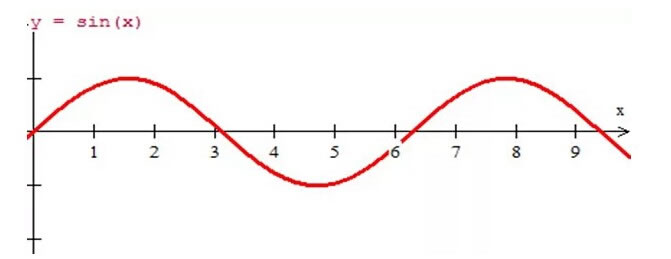
Figure 1 Fundamental wave
●What is harmonic
The definition of harmonic is "In a strict sense, harmonic refers to the amount of electricity contained in the current whose frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental wave.
Generally speaking, it refers to the amount of electricity generated by the Fourier series decomposition of periodic non-sinusoidal electricity, and the remaining current is greater than the fundamental frequency.
In a broad sense, since the effective component of the AC power grid is a single frequency of the power frequency, any component different from the power frequency can be called a harmonic. At this time, the meaning of the word "harmonic" has become somewhat inconsistent with the original meaning. It is precisely because of the broad concept of harmonics that there are "fractional harmonics", "interharmonics", "subharmonics" and so on".
This paragraph looks complicated, but in fact, it can be simply understood as "performing Fourier series decomposition of periodic alternating current, and obtaining components with frequencies that are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency (greater than 1) is the harmonic". As shown in Figure 2, it is the third harmonic. Harmonics are classified according to frequency into odd harmonics, even harmonics and interharmonics.
●Classification of harmonics
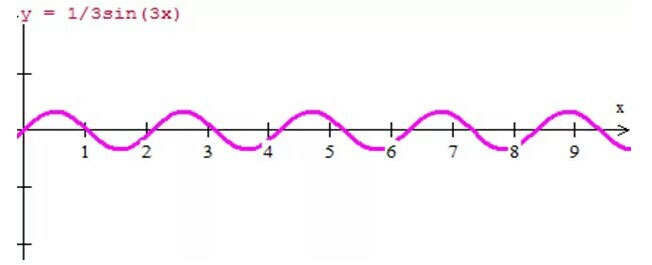
Figure 2 3rd harmonic
Odd harmonics - harmonics with a rated frequency that is an odd multiple of the fundamental frequency are called odd harmonics, such as 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics;
Even harmonics - harmonics with a rated frequency that is an even multiple of the fundamental frequency are called odd harmonics, such as 2nd, 4th, and 6th harmonics;
Interharmonics - harmonics with a frequency that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency are called simple harmonics, also called component harmonics.
As shown, this is the classification of harmonics by the power grid (50Hz).
●The impact of harmonics
Let's take a look at the impact of harmonics through a set of pictures. Add a 3rd harmonic to the fundamental wave of Figure 1, as shown in Figure 2, and you will get the waveform shown in Figure 4. When odd harmonics are superimposed, it becomes a square wave, as shown in Figure 5, which is the superposition of 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics. Figure 6 shows the waveform after superposition.
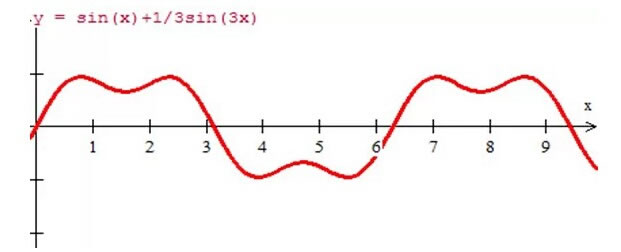
Figure 4 Waveform after superposition of 3rd harmonics
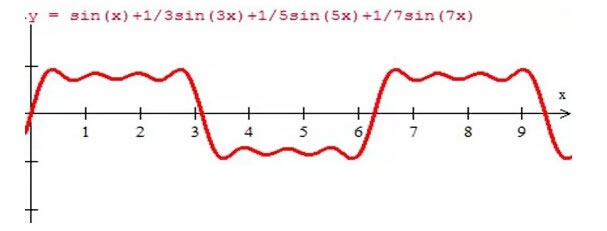
Figure 6 Waveform after superposition of 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics
Through the above waveform, we can see that due to the generation of harmonics and then superposition on the fundamental wave, the original fundamental wave has changed greatly, from the original sine wave to a square wave, which will not only reduce the system capacity such as transformers, circuit breakers, cables, etc., but also accelerate the aging of equipment, shorten the service life of equipment, and even damage equipment to endanger production safety and stability.
●How are harmonics generated?
So how are harmonics generated? After analysis, harmonics are mainly generated because the sine signal is pressed on the nonlinear load, and the fundamental current is distorted to generate harmonics. Common non-linear loads include UPS, switching power supplies, rectifiers, frequency converters, inverters, etc.
Therefore, this type of product needs to use a power analyzer to test its harmonics. In the future, we will introduce the advantages and disadvantages of harmonic testing of power analyzers from various manufacturers on the market.







