General Requirements of Safety Standards for A ppliances
The design and structure of the product must ensure that it will not cause electric shock and other hazards to the user under normal use and possible failure conditions, and will not cause harm to the surrounding environment, such as fire.
Basic Safety Principles
The following hazards should be avoided in product design and production:
●Electric shock and energy hazards
●Fire
●Heat hazards
●Mechanical hazards
●Radiation and chemical hazards
Electric Shock or Electric Shock
1. Fingers can touch parts with dangerous voltages through holes on the product.
2. External small conductors (such as bracelets) can touch conductors with dangerous voltages through small holes.
3. The insulation between components with dangerous voltages and safe low voltages is broken down, causing the accessible parts to carry dangerous voltages.
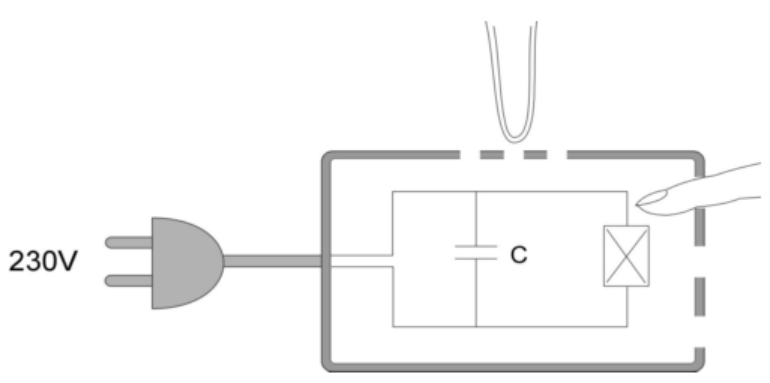
Discharge of Capacitors
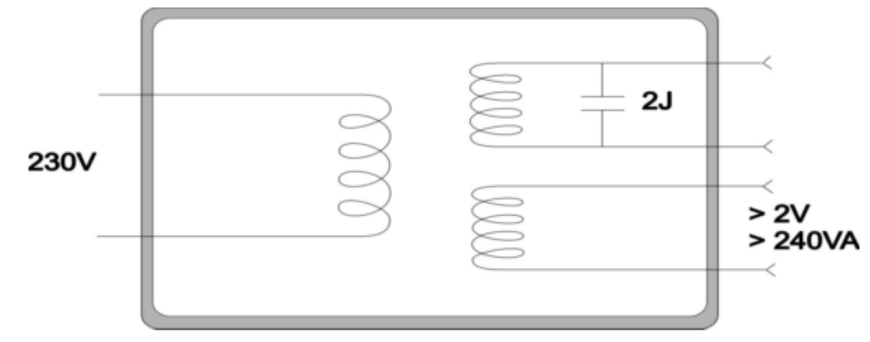
Although the output voltage is very low, if the conductor at the output end is short-circuited, it is possible to release excessive energy and even explode.
2J of energy is equivalent to a 3300mF capacitor with an energy storage of 35V.
Fire
●The biggest danger of electrical products is fire. The product spontaneously ignites and spreads to the surrounding environment. It will cause huge casualties and property losses.
●Plastic is the main cause of fire. If plastic is not treated with fireproofing, it will be the main source of fire.
●Overload, component failure, insulation breakdown, loose connection may generate temperature that leads to fire. If there is no protective measure, it will cause fire.
Heat Hazards
● If the temperature of the accessible parts is too high, it will burn the user
● The components in the equipment will be affected by long-term exposure to excessively high temperatures
● Insulating materials will have a risk of reduced insulation performance or even melting in a high-temperature environment

Mechanical Hazards
● Sharp edges may cause harm to the human body and damage to components.
● If moving parts (such as fan blades) are accessible, they may cause harm to the user.
● If the equipment is not placed stably, it may easily fall over, causing harm to the user and the surrounding environment.
● The shell material is not strong enough and may easily break under stress, causing dangerous live parts to be accessible.
● The power cord is not fixed reliably. If it is pulled out by external force, it may cause electric shock.
Radiation and Chemical Hazards
● X-ray radiation: CRT (cathode ray tube) should be less than <0.5mR/H.
● Laser hazards: The laser head of CD/VCD is generally required to be Class I, unless there is a special protective device and a warning sign.
● Toxic gases, liquids, dust, etc.

Abnormal Conditions
The product can still maintain its safety when the following abnormal conditions occur: Only one abnormal condition is assumed to occur at a time.
Component failure
The standard assumes that electronic components are unreliable and may fail.
Misuse
●The user may use the device incorrectly or not use it according to the instructions, such as:
-Not giving the device enough heat dissipation space, or the heat dissipation hole is accidentally blocked, causing excessive temperature.
-For short-time working equipment, the user ignores its working time. Continuous work causes excessive temperature
●Output end of the transformer, short circuit and overload.
●Motor overload or stall.
Insulation failure
●Only single insulation protection is considered unreliable, so the product's protection against electric shock cannot rely on single insulation.
●Additional protection measures must be provided, such as protective grounding or additional insulation.
●Of course, providing separate enhanced insulation protection with super performance is acceptable.
For detailed knowledge of insulation, we will analyze it later.
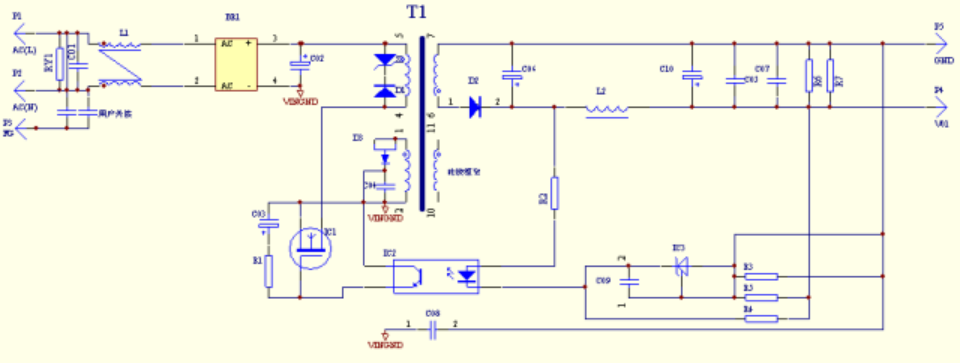
Circuit example
Connection failure
Solder connections may fail. For example:
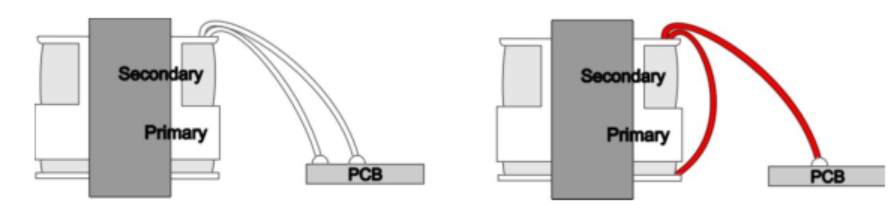
●Additional fixed protection should be provided at the connection, such as wire bundling, glue dripping, Hook welding, etc.
IP levels
Explanation of IP Numbers for Degrees of Protection.
The protection type is:
(a) Preventing people from touching or approaching live parts and touching movable parts, and preventing solid impurities from entering the equipment.
(b) Equipment IP XX to prevent water from entering.
The degree of protection indicated by the first characteristic number
0 -- No protection, that is, no special protection performance.
1 -- Preventing the entry of solid objects over 50 mm.
2 -- Preventing the entry of solid objects over 12 mm.
3 -- Preventing the entry of solid objects over 2.5 mm.
4 -- Preventing the entry of solid objects over 1.0 mm.
5 -- Dustproof, that is, it cannot completely prevent the entry of dust, but the amount of dust entering will not affect the normal operation of the equipment.
6 -- Sealed dustproof, that is, no dust enters and works under a certain water pressure without any harmful effects.
The second characteristic number indicates the degree of protection
0 -- No protection, i.e. no special protection.
1 -- Water droplets (vertically falling water droplets) have no harmful effects.
2 -- Rainproof, tilted 15, rain test has no harmful effects.
3 -- Spraying water, i.e. water has no harmful effects when it is sprinkled at an angle of 60 degrees to the vertical direction.
4 -- Splashing water, i.e. water has no harmful effects when it splashes on the shell from all directions (360).
5 -- Water spraying, i.e. water spraying from all directions with a nozzle should have no harmful effects.
6 -- Sealed, i.e. when the product can be immersed in water for work, there is no danger.
8 -- Pressure sealing, i.e. the equipment is suitable for continuous immersion in water under the conditions specified by the manufacturer.






