Definition of terms
Each term has a clear definition in the standard. When reading the standard and test report, if the definition is not clear, there will be some difficulties and misunderstandings. Therefore, some important and easily misunderstood terms are explained as follows:
● Rated voltage/voltage range:
The manufacturer's nominal equipment supply voltage or voltage range. For three-phase electricity, it refers to the line-to-line voltage
● Rated current:
The manufacturer's nominal maximum input current of the equipment during normal operation
● Rated frequency/range:
The manufacturer's nominal equipment supply frequency or frequency range
● Rated working time:
The equipment working time specified by the manufacturer
● Rated load:
The normal load conditions specified in the equipment manual
Classification of equipment housing
● Mechanical housing:
A housing that reduces mechanical and physical damage
● Fireproof housing:
A housing that prevents the spread of flames
● Electrical housing:
A housing that limits contact with dangerous voltages or dangerous energy
● Decorative parts:
A component of the equipment housing that does not play a safety role

Grounding and leakage current
● Functional earthing:
A grounding point on the equipment that is not for safety
● Protective earthing terminal:
A terminal used to connect to the building grounding pile
● Protective bonding:
Connected to the protective earth path to achieve the function of safe protective earthing
● Touch current:
A component of the equipment housing that does not play a safety role ... Functional earthing terminal:
A terminal used to connect to the building grounding pile
● Protective bonding:
Connected to the protective earth path to achieve the function of safe protective earthing
● Touch current:
A component of the equipment housing that does not play a safety role Current: The current flowing through the human body. Leakage current: (Old term) Test classification. Type test: A test conducted on a representative sample according to a standard. Sampling test: A test on a sample randomly selected from a batch of products. Routing test: 100% inspection (on the main production line). Equipment classification by mobility. Movable equipment: 18kg, not fixed or with wheels for easy mobility. Hand-held equipment: Movable equipment, handheld use. Transportable equipment: Movable equipment carried by the user. Stationary equipment: Not movable when in use. Building-in equipment: Direct plug-in equipment: No wires. Equipment classification by power connection method. Pluggable equipment Type A equipment A):
Non-industrial plugs and sockets, non-industrial coupling devices
●Pluggable Equipment Type B:
Non-industrial plugs and sockets, non-industrial coupling devices (compliant with IEC60309)
●Permanently Connected Equipment:
Fixed connection by screws or equivalent methods
●Detachable Power Supply:
●Detachable Power Supply:
Basic safety electrical terms
●Working voltage:
Under normal working conditions, the maximum voltage that an insulation or component needs to withstand
Including: Vrms and Vpeak
●Hazardous voltage: >42.4Vac or 60Vdc (IEC/EN60950)
>35Vpeak or 35Vdc (IEC/EN60065)
Can cause electric shock hazards
●Safety low voltage (SELV)
Voltage: <42.4Vac or 60Vdc (IEC/EN60065)
<35Vpeak or 35Vdc (IEC/EN60065)
Isolated from the mains power supply by double insulation or reinforced insulation
Several types of safety circuits
●AC Mains Supply:
External AC power supply system that powers the equipment
●Primary Circuit:
Circuit directly connected to the AC mains power supply
●Secondary Circuit:
Circuit not directly connected to the primary circuit but powered by an isolation device or battery
Several types of safety circuits
●Safety Isolated Low Voltage Circuit (SELV)
A properly designed and protected secondary circuit, so that under normal conditions or single fault conditions, its output voltage is less than 42.4Vac and 60Vdc (IEC/EN60950) (or 35Vpeak and 35Vdc ((IEC/EN60065)), and is isolated from the mains power supply by double insulation or reinforced insulation
●Current Limiting Circuit
A properly designed and protected circuit, so that under normal conditions or single fault conditions, the output voltage of the secondary circuit is less than 42.4Vac and 60Vdc (IEC/EN60950) (or 35Vpeak and 35Vdc ((IEC/EN60065)), and is isolated from the mains power supply by double insulation or reinforced insulation
●Current Limiting Circuit
A properly designed and protected circuit, so that under normal conditions or single fault conditions, the output voltage of the secondary circuit is less than 42.4Vac and 60Vdc (IEC/EN60950) (or 35Vpeak and 35Vdc ((IEC/EN60065)), and is isolated from the mains power supply by double insulation or reinforced insulation The current value flowing out of the circuit is a non-hazardous current value. Generally, for frequencies less than 1kHz, the steady-state current through a 2000W resistor is less than 0.7mA. ● Communication network voltage circuit (TNV)
Under normal conditions, circuits connected to public or private communication networks, communication networks may be over-voltage caused by atmospheric discharge and wire failures.
Several types of safety circuits
Insulation categories
● Basic insulation
Insulation added to live parts to provide basic protection against electric shock
● Supplementary insulation
Independent insulation that provides protection against electric shock when basic insulation fails
● Double insulation
Insulation composed of basic insulation and supplementary insulation
● Reinforced insulation
A single insulation system added to live parts that provides a level of protection against electric shock equivalent to double insulation
Insulation diagram
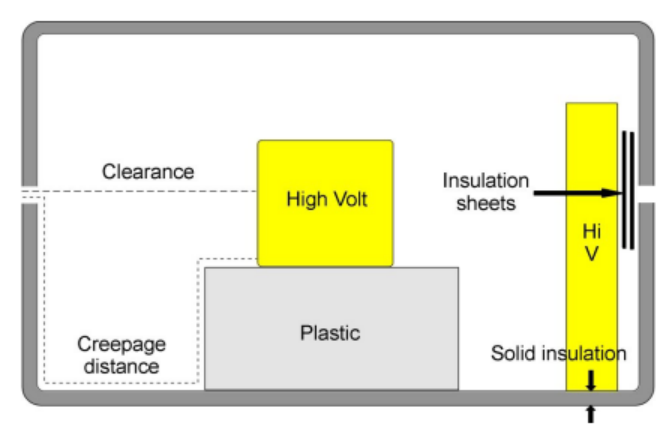
Creep distance and space clearance
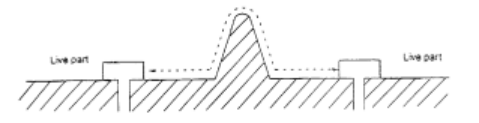
● Creepage distance (Cl)
The shortest distance along the surface of the insulator between live parts or between live parts and accessible surfaces
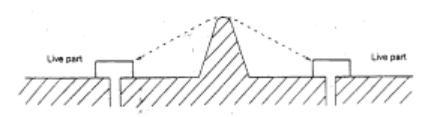
● Space clearance (Cr)
The shortest distance between live parts or between live parts and accessible surfaces
Classification by protection against electric shock category
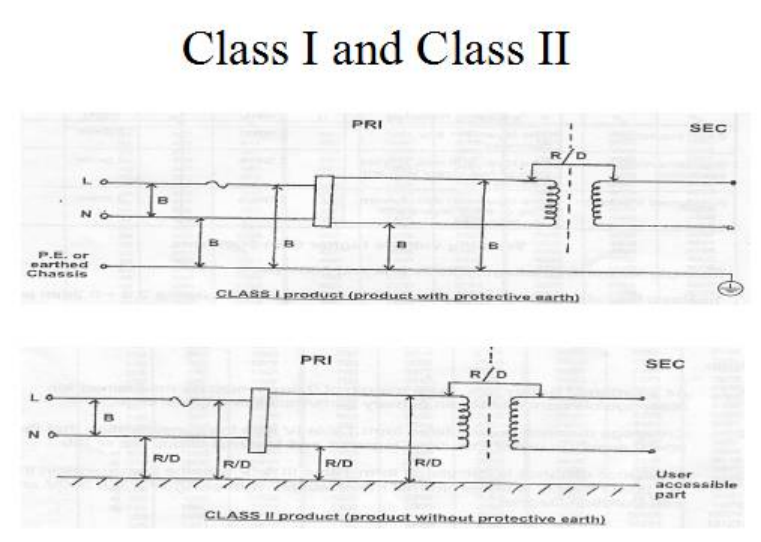
● Class I Equipment:
Products are protected against electric shock by basic insulation plus protective earthing.
●Class II Equipment:
Products are protected against electric shock by basic insulation plus supplementary insulation, or by reinforced insulation.
●Class III Equipment:
Products are protected against electric shock by safety low voltage (SELV).
Example of equipment protection against electric shock
Basic insulation and double insulation







