Anyone who use electricity has heard of the term three phase and single phase , maybe trying to understand the circuit, fundamental difference between them but unclear where to start, this essay narrates everything you want to know about three-phase electricity and single-electricity.
What does 'phase' mean?
Before we start, it is important to understand what the term 'phase' means. In electricity, The phase refers to the distribution of a load. The word 'phase' can refer to a relative variation, a change of state, or a cycle. It can refer to a change in state or anything else with respect to time. In electrical engineering, phase refers to the pattern by which the sinusoidal voltage of an AC supply shifts between its positive and negative maximums.
A three-phase supply consists of three sinusoidal patterns that are 120 degrees out of phase with each other. A single-phase supply consists of one of these three patterns, along with a neutral wire. Both single-phase and three-phase supplies have roles for which they are well suited. At the same time, they differ from each other. This article provides a clear explanation of the differences between single-phase and three-phase supplies. The figure below shows the phase rotation in a three-phase system.
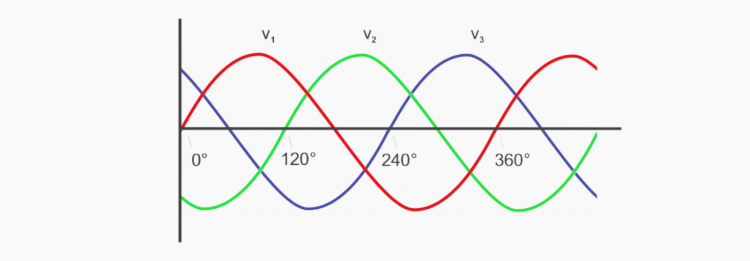
Next, we will analyse the main differences between single-phase and three-phase electricity in terms of efficiency and other factors.
Efficiency
Three-phase power is more efficient. Three-phase power can transmit three times the power of single-phase power with only one additional wire. For example, elevators in high-rise buildings use three-phase systems. Therefore, whether it is three-wire or four-wire three-phase power, it uses less conductor material than single-phase power to transmit the same amount of electricity.
Voltage rating
Single-phase electricity typically has a voltage of 220V, while three-phase electricity typically has a voltage of 380V.
Stability of power transmission
Due to voltage fluctuations, single-phase power sources are less stable than three-phase power sources. For example, when starting a vacuum cleaner, the lights may temporarily dim. Three-phase power sources transmit power at a stable, constant rate, enabling uninterrupted operation of equipment such as MRI machines in hospitals.
Power supply wiring requirements
Single-phase power requires only two wires: a phase wire and a neutral wire, such as those used in standard household sockets for lighting and mobile phone chargers. On the other hand, three-phase power requires only three wires — one neutral wire and two three-core wires — to operate.Therefore, when you directly supply three-phase power to server cabinets, both wiring costs and overall installation costs are reduced (e.g., three-phase wiring for server racks in data centres).
Three-phase power is widely used in commercial and industrial environments due to its inherent advantages over single-phase power systems. Three-phase power systems are much more efficient at transmitting electricity, which is particularly beneficial for equipment that requires high power, such as industrial motors and large electrical machinery. This efficiency stems from the continuous power generation capability of three-phase systems, which ensures that power peaks are more evenly distributed and energy transmission is more stable.The phase separation in a three-phase system enables nearly constant power output. This balance is critical in situations where machinery must operate continuously without interruptions or power degradation, a common issue in single-phase systems. Three-phase systems are more cost-effective for long-distance power transmission. Compared to single-phase systems, the same amount of power transmission requires less conductor material, thereby reducing overall infrastructure costs. Equipment powered by three-phase power operates more smoothly due to balanced power supply, resulting in reduced stress. This extends equipment lifespan and lowers maintenance costs.
Three-phase power is the main power supply method in industry. It's the preferred choice for driving large-scale equipment, data centres and manufacturing because it's highly efficient, has high power density and a stable output. Three-phase power is great for continuous and stable energy transmission because it uses three sets of alternating current waveforms with a phase difference of 120°. It can transmit more than three times the power of single-phase power with fewer conductors, while also reducing transmission losses significantly.
Three-phase DC power supply use the benefits of three-phase power to improve energy conversion solutions even more. They use efficient rectification technologies (like six-pulse rectification or active PFC) to convert three-phase AC power into ultra-low ripple DC power, making them perfect for demanding applications such as high-precision industrial equipment, electric vehicle fast charging, and semiconductor manufacturing. Compared to traditional single-phase rectification solutions, Three-phase DC power supplies offer a range of advantages compared to their single-phase counterparts:

Higher Efficiency: The three-phase system can deliver more power with greater efficiency, which can translate into cost savings for users.
Less Voltage Loss: Due to the lower current load, voltage drop is minimized in three-phase systems.
Improved Stability: The continuous supply from three phases results in improved stability and reliability.
Better Load Distribution: Three-phase systems balance loads across their phases, reducing strain on any one phase and improving longevity.
Finally, if you have any questions about this article or would like to purchase DC power supplies or other electrical products, please feel free to contact us!








