DC/DC converters are crucial electronic components in modern electronic devices. Let's learn about them today.
I. What is a DC/DC Converter?
A DC/DC converter is a component that converts DC (direct current) to DC (direct current). Specifically, it refers to a component that converts voltage using DC (direct current). Electronic components such as ICs have different operating voltage ranges, so they need to be converted to the appropriate voltage.
Converters that generate a voltage lower than the initial voltage are called "buck converters"; converters that generate a voltage higher than the initial voltage are called "boost converters."
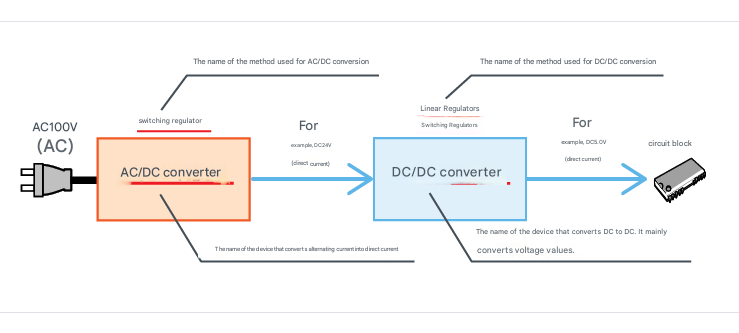
A DC/DC converter is the name for a device that converts DC to DC.
It is often referred to as a linear regulator or a switching regulator, depending on the conversion method used.
Power supply devices that lower voltage include step-down converters, buck converters, and step-down converters. Power supply devices that increase voltage include step-up converters, boost converters, and step-up converters. Power supply devices that step up and down voltage include step-up and down converters, buck-boost converters. Power supply devices that generate negative voltage include negative voltage converters, inverter converters, and inverter converters.
II. About AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current)
What is AC?
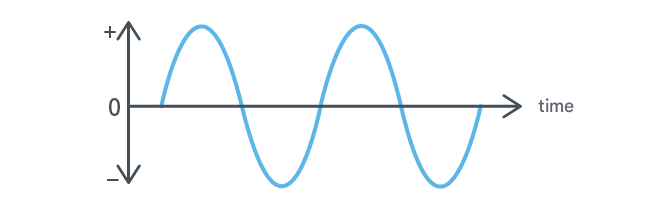
Alternating Current (AC) is the acronym for alternating current.
AC is an electric current whose magnitude and polarity (direction) change periodically over time.
The number of times the current's polarity changes in one second is called frequency, expressed in Hz.
What is DC?
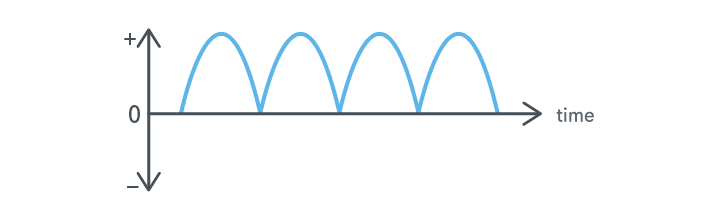
Alternating Current (DC) is the acronym for direct current.
DC is an electric current whose polarity (direction) does not change over time.
① Current flowing with a constant polarity (direction) and magnitude is generally referred to as DC.

② Current whose polarity remains constant but whose magnitude varies with time is also DC and is commonly referred to as ripple current.
III. Why Do We Need a DC/DC Converter?
Electrical products that plug into an outlet require an AC/DC converter to convert 100V AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current).
This is because most semiconductor components operate only with DC.
ICs and other components mounted on a device's circuit board each have their own unique operating voltage ranges and voltage accuracy requirements.
Powering a device with unstable voltage can cause malfunctions or characteristic degradation.
For this reason, a DC/DC converter is required to convert the voltage to the required level and stabilize it.
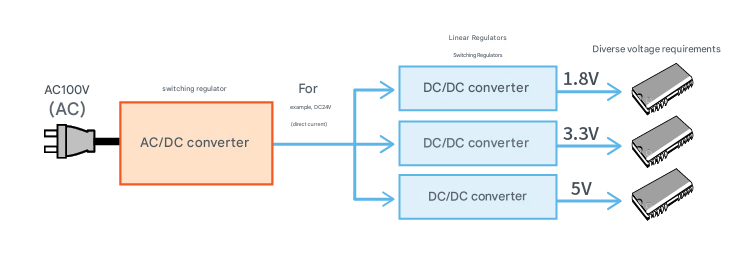
Device that stabilizes voltage using a DC/DC converter is called a voltage regulator.
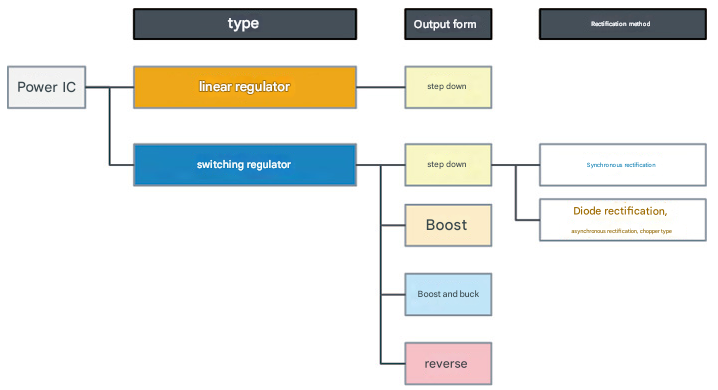
IV. Types of Power Supply ICs
Power supply ICs are broadly classified into two types: linear regulators and switching regulators.
As for their respective output formats, linear regulators can only step down the output voltage to a lower level than the input voltage. Switching regulators offer flexibility, with four output types:
Step-down (outputting a voltage lower than the input voltage)
Step-up (outputting a voltage higher than the input voltage)
Step-up (outputting a constant voltage, regardless of the input voltage)
Reversing a positive voltage to output a negative voltage
Furthermore, switching regulators have two rectification methods: synchronous rectification and asynchronous rectification (diode rectification).
V. Linear Regulators and Switching Regulators
Device that stabilizes voltage using a DC/DC converter is called a voltage regulator.
Based on the conversion method, voltage regulators are divided into two types: linear regulators and switching regulators.
Linear Regulators
Because the relationship between input and output is linear during operation, they are called "linear regulators."
Because a control element is connected in series between the input and output, they are sometimes called "series regulators."
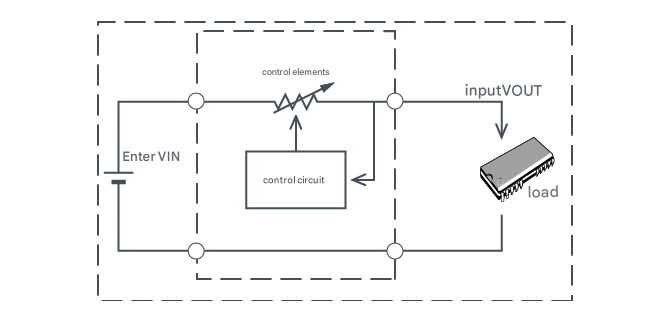
Because the voltage is stepped down by the control element, the larger the voltage difference between the input and output (the degree of step-down), the greater the loss and the lower the efficiency.
Thus, they are suitable for low-power power supplies.
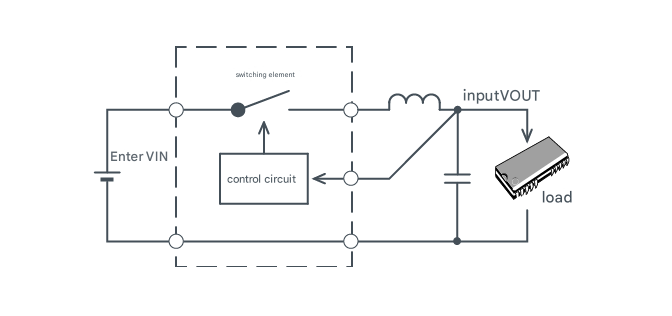
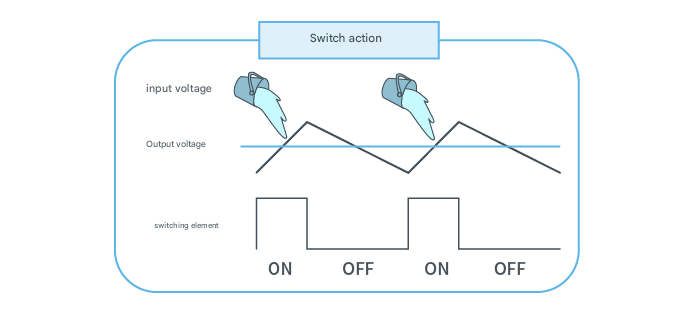
Switching Regulator
The switching element (MOSFET) is turned on, transferring power from the input to the output until the output voltage reaches the desired value.
Once the output voltage reaches the specified value, the switching element turns off, dissipating no more input power.
By repeating this action at high speed, the output voltage is regulated to the specified value.
VI. Operating Principle of Linear Regulators
General Pin Configuration
A linear regulator basically consists of three pins: VIN (input), VO (output), and GND (ground).
Variable-output linear regulators have an FB (feedback) pin added for output voltage feedback.
Simply put, a fixed-voltage regulator is a regulator with a built-in variable-voltage external resistor.
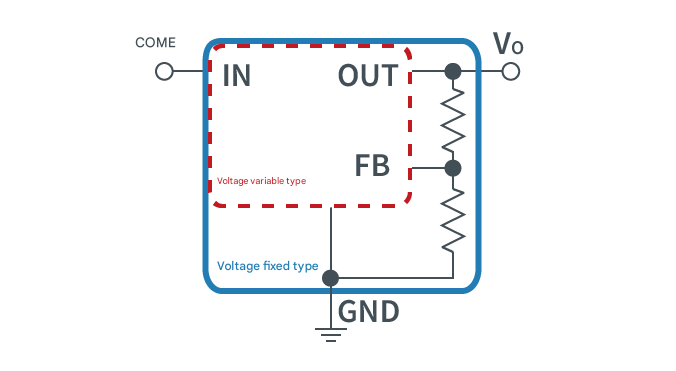
Internal Circuit
The following figure shows an overview of the internal circuit of a linear regulator.
The operating principle is similar to that of an inverting amplifier circuit. The voltage at the non-inverting pin (FB) of the error amplifier is equal to the reference voltage (VREF), so the output voltage (VO) is determined by the resistance ratio of the two resistors (R1 and R2).
Vo = [ (R1 + R2) / R2 ] x VREF
The output transistor in the figure below is a MOSFET, but there are also products using bipolar transistors.
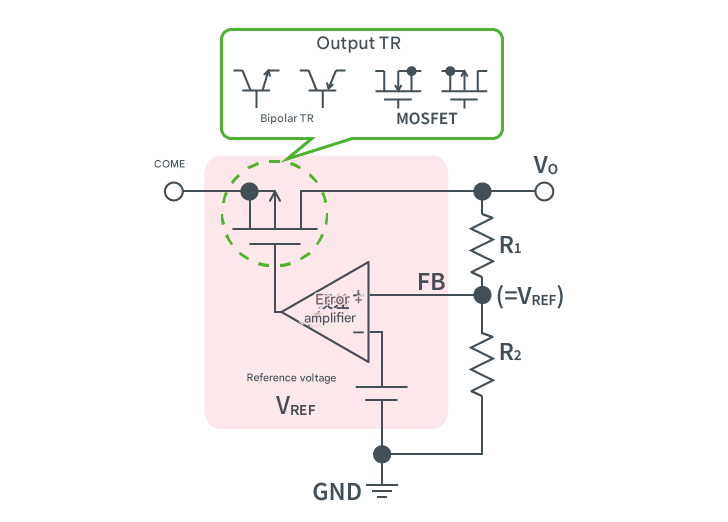
This detailed, step-by-step explanation provides a deeper understanding of what a DC-DC converter is. DC-DC converters are widely used in various fields and have become an indispensable component of modern electronic systems.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media














